AI-Powered Healthcare Analytics
Platform for HCP Management
Discover, Profile and Engage the right
Healthcare Professionals
HCP Payments
Clinical Studies
Medical Journal Articles
Sanctions
Patents
Global Medical Events
Grants
Life Science Journals

Get connected to over 2 Million Medical Experts across diverse therapeutic areas through our AI-Powered Platform!



Key Opinion Leader Management for Every Department
Empowering Life Sciences teams with Intelligent Analytics and Advanced Tools.
Medical Teams
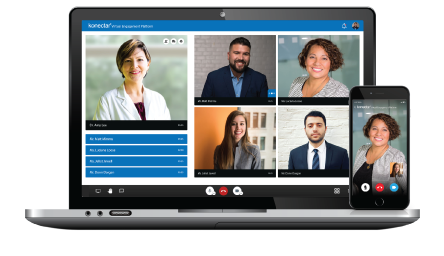
Our Healthcare Analytics Platform is designed specifically for the Medical / Field Medical Teams to identify and engage the right medical experts for different stages of drug development. konectar helps in transforming the Medical Affairs processes and developing the most effective communication strategies with KOLs.
Clinical Teams
With advanced techniques, konectar provides unmatched support for Clinical Teams. konectar's Industry Payments Analytics feature helps Clinical Teams to gain valuable insights into healthcare data, average spends on medical experts, and overall HCP utilization across various engagements.
Commercial Teams
Using Machine Learning technology, konectar makes it easier for Commercial Teams to segment the HCPs into prescribers, researchers, and global and regional speakers. konectar's Speaker Bureau Management feature helps Commercial Teams to connect with influential speakers and plan their Speakers' Bureau Program.
Establish successful Industry-HCP relationships by identifying and engaging the right experts.
-
Robust KOL Tiering Algorithms
-
Global, National, and Regional Thought Leaders
-
Segmentation based on Disease Expertise and Experience
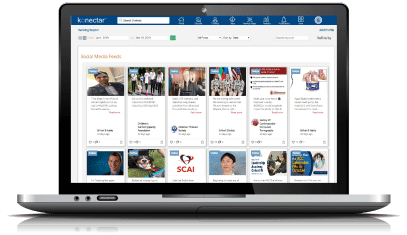
Discover the right healthcare experts for your business objectives. Our advanced platform scours the entire web and analyzes every single HCP profile to identify the right individuals with expertise that align with your goals.

Discover high-potential experts with proven track record through objective, data-driven analysis.

Segment the experts based on activities and expertise by assigning weightages to different criteria.
Identify the national and local influencers based on direct feedback from the physicians.
Develop more productive interactions by gaining a deep understanding of your Healthcare Professionals.
-
360-degree Expert Profiling
-
Influence Mapping and Network Analysis
-
Continually updated Customer Data
Profile the healthcare experts, so you have a good understanding of their professional interests, scientific research, networks, and connections.
Get a solid understanding of your medical professionals’ background through accurate and comprehensive profiles.

Understand your HCPs and their professional interests, networks and connections through visualizations and reports.
Stay updated on the evolving professional activities and accomplishments of your healthcare experts with real-time updates.
Explore and navigate different features of the Healthcare Analytics Platform seamlessly
-
Intuitive and Easy-to-Use
-
Mobile-friendly Interface
-
Brilliant Visualization
Engage your healthcare specialists in productive and fruitful partnerships through an approach based on a solid understanding of their areas of interests. Track the progress in engagement and measure over time to ensure maximum ROI.

Customize the modules as per your compliance and process needs, and track ongoing engagement.
Understand the professional networks, connections and collaborations within the community.
Seamlessly integrate with your existing CRM applications and view data in a single application.
Discover
Profile
Engage
The right Key Opinion Leaders
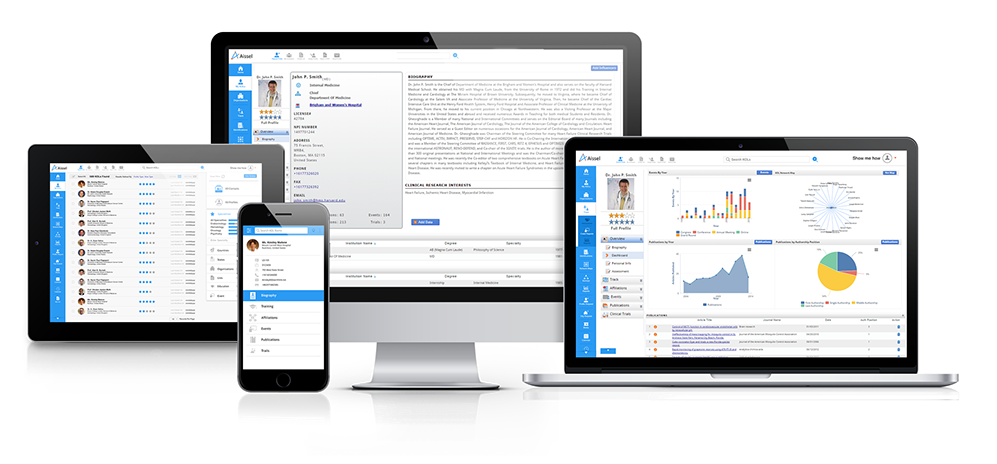
Access profiles of thousands of Healthcare Professionals
Request a DemoMore Specialties
- Anesthesiology
- Animal Health
- Cardiology
- Dentistry
- Dermatology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Disease
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Pediatrics
- Psychiatry
- Pulmonology
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- Geriatrics
- Gynecology
- Hematology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Health
- Orthopaedics
- Obstetrics
- Radiology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Surgery
- Urology